Report on Nasogastric (NG) Tube Insertion
Title: Report on Nasogastric (NG) Tube Insertion
Introduction: The purpose of this report is to provide an overview of nasogastric (NG) tube insertion. This procedure is commonly performed in healthcare settings to provide enteral nutrition, decompress the stomach, or administer medications. Understanding the anatomy and physiology, indications, contraindications, procedure, advantages, disadvantages, nursing management, and conclusion of NG tube insertion is essential for healthcare professionals involved in the process.
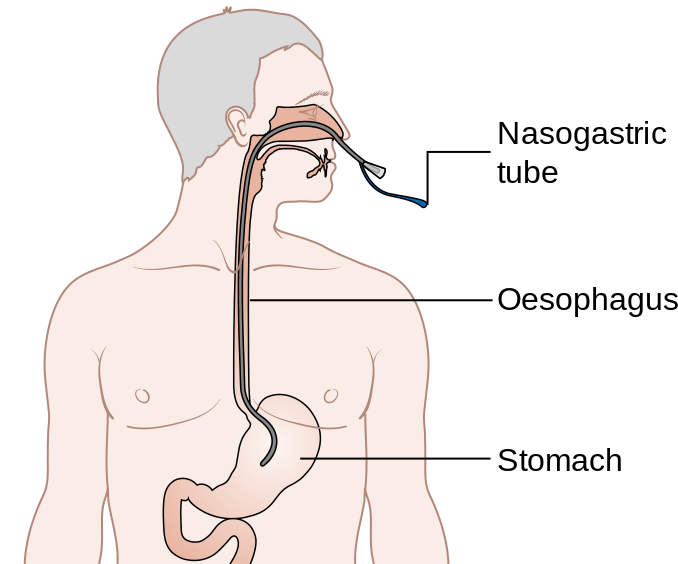
Anatomy and Physiology: The nasal cavity, pharynx, and esophagus are relevant anatomical structures involved in NG tube insertion. The nasal cavity serves as the entry point for the tube, while the pharynx and esophagus guide the tube towards the stomach. It is crucial to be aware of potential anatomical variations and obstructions that may affect the passage of the NG tube.
Physiologically, the stomach is responsible for receiving and digesting food. NG tube insertion allows access to the stomach for various purposes, such as providing nutrition or decompressing gastric contents.
Indications: NG tube insertion may be indicated for the following reasons:
- Enteral feeding in patients unable to take oral nutrition.
- Decompression of the stomach to relieve gastric distension or prevent aspiration.
- Administration of medications that cannot be given orally.
- Gastric lavage in cases of poisoning or overdose.
- Diagnosing gastrointestinal bleeding or other gastric abnormalities.
Contraindications: There are a few contraindications to consider when deciding on NG tube insertion:
- Severe facial trauma or recent nasal surgery.
- Basilar skull fracture or suspected head or neck injury.
- Esophageal obstruction or stricture.
- Recent gastric or esophageal surgery.
- Coagulopathy or bleeding disorders.
- Uncooperative or agitated patients who pose a risk of tube removal.
Procedure: The procedure for NG tube insertion typically involves the following steps:
- Explain the procedure to the patient and obtain informed consent.
- Gather the necessary equipment, including the NG tube, water-soluble lubricant, a cup of water, a syringe, and adhesive tape.
- Position the patient upright, with the head slightly tilted back.
- Measure the tube by placing it from the tip of the nose to the earlobe and then to the xiphoid process.
- Lubricate the tip of the tube.
- Insert the tube through the nostril and advance it gently towards the pharynx.
- Instruct the patient to swallow or sip water while slowly advancing the tube towards the stomach.
- Verify the tube's placement by aspirating gastric contents and confirming pH levels or through radiographic imaging.
- Secure the tube to the patient's nose using adhesive tape.
Advantages: NG tube insertion offers several advantages, including:
- Non-invasive procedure compared to surgical interventions.
- Provides a route for enteral nutrition when oral intake is not possible.
- Facilitates gastric decompression, reducing the risk of aspiration and promoting patient comfort.
- Allows administration of medications and treatments directly to the stomach.
Disadvantages: Despite its advantages, NG tube insertion also has some limitations and disadvantages, such as:
- Potential discomfort and irritation to the nasal passages and throat.
- Risk of misplacement or malpositioning, leading to inaccurate results or complications.
- Increased risk of nasopharyngeal trauma or bleeding during the insertion process.
- Patient discomfort and the possibility of accidental removal of the tube.
Nursing Management: Effective nursing management is crucial for successful NG tube insertion and subsequent care. Key aspects of nursing management include:
Assessment: Perform a thorough assessment of the patient, including their medical history, current condition, and any contraindications or precautions. Assess the patient's nasal patency, ability to swallow, and level of consciousness.
Patient Education: Explain the purpose, procedure, and potential complications of NG tube insertion to the patient and obtain informed consent. Provide clear instructions on how to cooperate during the procedure and manage the tube afterwards. Educate the patient on signs of complications to report.
Preparation: Ensure all necessary equipment is readily available. Gather the appropriate-sized NG tube, lubricant, water, syringe, and tape. Verify the correct placement of the tube before securing it.
Procedure Assistance: Assist the healthcare provider during the insertion procedure by providing appropriate patient positioning, offering support and reassurance to the patient, and facilitating the swallowing process if necessary.
Monitoring: Regularly monitor the patient's vital signs, respiratory status, and comfort level during and after the procedure. Observe for any signs of complications, such as respiratory distress, coughing, or nasal bleeding.
Documentation: Accurately document the procedure, including the size and type of NG tube inserted, the length of insertion, method of verification, patient response, and any complications or adverse events. Document ongoing assessment findings, intake and output measurements, and the patient's tolerance of the tube.
Conclusion: NG tube insertion is a commonly performed procedure in healthcare settings for enteral feeding, gastric decompression, and administration of medications. Understanding the anatomy and physiology, indications, contraindications, procedure, advantages, disadvantages, nursing management, and conclusion of NG tube insertion is essential for healthcare professionals. By ensuring proper patient assessment, education, preparation, assistance, monitoring, and documentation, nurses can contribute to the safe and effective implementation of NG tube insertion and subsequent patient care.
References: (These references are provided in APA format.)
Brown, C. A. (2020). Nasogastric tube insertion. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing.
Cohen, R. D., & Woods, A. (2021). Nasogastric and nasoenteric feeding tubes: Placement, management, and complications. In UpToDate. Retrieved from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/nasogastric-and-nasoenteric-feeding-tubes-placement-management-and-complications
Potter, P. A., Perry, A. G., Stockert, P. A., & Hall, A. M. (2021). Fundamentals of nursing. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Smeltzer, S. C., Bare, B. G., Hinkle, J. L., & Cheever, K. H. (2019). Brunner & Suddarth's textbook of medical-surgical nursing. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Swift, A., & Nichols, J. (2017). An overview of nasogastric tube insertion and management. British Journal of Nursing, 26(19), S16-S21.


No comments