Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (S-ICD)
Title: Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (S-ICD)
Introduction: The subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (S-ICD) is a relatively new technology developed for the prevention of sudden cardiac death. Unlike traditional implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs), the S-ICD is placed entirely subcutaneously, eliminating the need for intravascular leads and reducing associated complications. This report aims to provide an overview of S-ICD, including its anatomy and physiology, purpose, indications, contraindications, advantages, disadvantages, equipment, patient preparation, procedure, risks, complications, nursing interventions, patient teaching, nursing management, and conclusion.
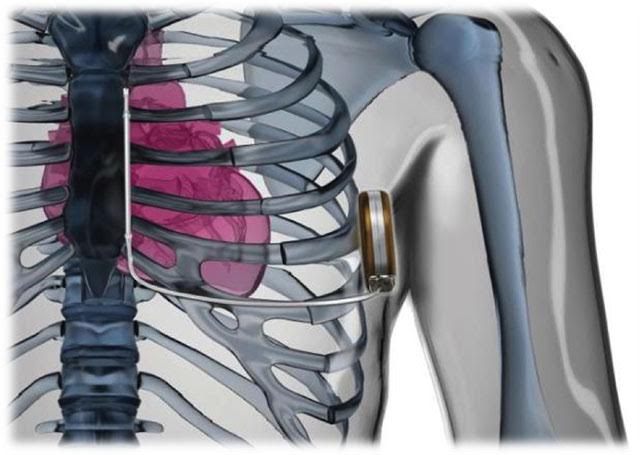
Anatomy and Physiology: The S-ICD system consists of a pulse generator, which is placed subcutaneously in the left parasternal region, and a subcutaneous electrode, which runs along the left sternal border. The electrode detects ventricular arrhythmias and delivers a high-energy shock to restore normal heart rhythm. The Subcutaneous placement avoids the risks associated with intravascular leads, making it an attractive option for some patients.
Purpose: The primary purpose of S-ICD is to prevent sudden cardiac death in patients at risk of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias. It is indicated for patients who do not require pacing and who have no need for anti-tachycardia pacing.
Indications: The S-ICD is indicated in patients who meet the following criteria:
- Patients with a history of sustained ventricular arrhythmias or cardiac arrest.
- Patients at high risk of sudden cardiac death due to specific conditions such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, long QT syndrome, or Brugada syndrome.
- Patients with certain structural heart diseases or previous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator explantation.
Contraindications: The S-ICD may not be suitable for patients who meet the following contraindications:
- Patients requiring pacing therapy for bradycardia or heart failure.
- Patients with pre-existing leads or devices that are incompatible with the S-ICD system.
- Patients with significant obesity or excess subcutaneous adipose tissue in the device implantation area.
Advantages: The S-ICD offers several advantages over traditional transvenous ICDs, including:
- Reduced risk of lead-related complications such as infection, lead dislodgement, and venous thrombosis.
- Avoidance of intravascular leads and their associated long-term complications.
- Simpler implantation procedure, often requiring less time and fluoroscopy.
- Potential for easier system removal or upgrade if necessary.
Disadvantages: Despite its advantages, the S-ICD has some limitations:
- Inability to provide pacing therapy, limiting its use in patients requiring resynchronization or bradycardia support.
- Limited ability to discriminate supraventricular from ventricular tachycardias, leading to higher inappropriate shock rates.
- The device is larger and bulkier than traditional ICDs due to the subcutaneous placement.
Equipment: The equipment required for S-ICD implantation includes:
- S-ICD pulse generator.
- Subcutaneous electrode.
- Sterile surgical drapes, gloves, and gowns.
- Sterile instruments for surgical site preparation and device implantation.
- Suturing materials.
- Sterile dressings.
Preparing the Patient: Preparation for S-ICD implantation involves several steps, including:
- Comprehensive patient assessment, including medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
- Explanation of the procedure, risks, benefits, and expected outcomes to the patient.
- Ensuring the patient is well-informed and has provided informed consent.
- Pre-operative laboratory tests, electrocardiogram, and imaging studies as indicated.
- Pre-operative fasting to minimize the risk of aspiration during the procedure.
Procedure: The S-ICD implantation procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Administering local anesthesia to the left parasternal region.
- Creating an incision to accommodate the pulse generator placement.
- Tunneling the subcutaneous electrode along the left sternal border.
- Verifying appropriate placement and function of the S-ICD system using fluoroscopy and electrocardiography.
- Closing the incisions and applying sterile dressings.
Risks and Complications: Potential risks and complications associated with S-ICD implantation include:
- Infection at the incision site.
- Bleeding or hematoma formation.
- Device-related complications such as migration or erosion.
- Nerve or muscle damage during the electrode placement.
- Inappropriate shocks due to the inability to discriminate arrhythmias accurately.
Nursing Interventions: Nursing interventions related to S-ICD implantation include:
- Pre-operative patient education and support.
- Monitoring vital signs and assessing the incision site for signs of infection or complications.
- Assisting with pain management and providing comfort measures.
- Educating the patient on proper care and maintenance of the S-ICD system.
- Ensuring the patient understands the importance of regular follow-up visits.
Nursing Patient Teaching: Patient teaching after S-ICD implantation should include:
- Explanation of the purpose and function of the S-ICD system.
- Recognition and management of potential device-related complications.
- Education on appropriate responses to shocks and when to seek medical assistance.
- Instructions on regular wound care and signs of infection.
- Importance of attending follow-up appointments and regular device checks.
Nursing Management: Nursing management of patients with S-ICD includes:
- Monitoring and documenting the patient's clinical status and device function.
- Collaborating with other healthcare providers to ensure appropriate programming of the S-ICD system.
- Providing ongoing patient education and support.
- Addressing any psychosocial concerns or anxiety related to the device.
- Facilitating access to support groups or resources for patients with implanted devices.
Conclusion: The subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (S-ICD) offers an alternative option for the prevention of sudden cardiac death in eligible patients. While it provides advantages such as reduced lead-related complications, it also has limitations, including the lack of pacing capabilities. Nurses play a crucial role in the pre-operative, peri-operative, and post-operative care of patients undergoing S-ICD implantation, providing education, monitoring, and ongoing support.
Reference's
Olde Nordkamp LR, Dabiri Abkenari L, Boersma LV, et al. The entirely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator: initial clinical experience in a large Dutch cohort. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(19):1933-1939. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2012.07.030
Burke MC, Gold MR, Knight BP, et al. Safety and efficacy of the totally subcutaneous implantable defibrillator: 2-year results from a pooled analysis of the IDE study and EFFORTLESS registry. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65(16):1605-1615. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2015.02.065
Weiss R, Knight BP, Gold MR, et al. Safety and efficacy of a totally subcutaneous implantable-cardioverter defibrillator. Circulation. 2013;128(9):944-953. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.002686
Lambiase PD, Barr C, Theuns DA, et al. Worldwide experience with a totally subcutaneous implantable defibrillator: early results from the EFFORTLESS S-ICD Registry. Eur Heart J. 2014;35(25):1657-1665. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehu119
Priori SG, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Mazzanti A, et al. 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: the Task Force for the Management of Patients with Ventricular Arrhythmias and the Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2015;36(41):2793-2867. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehv316


No comments